Proper electrical contactor wiring isn’t just technical—it’s financial armor for industrial operations. Imagine a single miswired terminal in a 480V system causing $18k in motor repairs. That’s not fearmongering; 68% of motor control failures trace back to flawed contactor installations (IEEE 2024). As an electrician, I’ve seen how rushed wiring compromises safety and budgets. This guide delivers field-tested methods, compliance checklists, and actionable diagrams to master electrical contactor setups. We’ll demystify coil voltage mismatches, torque specs for 400A lugs, and phase rotation errors—no jargon, just precision. Ready to turn complex schematics into muscle memory? Let’s wire smarter, not harder.
What is a Contactor?
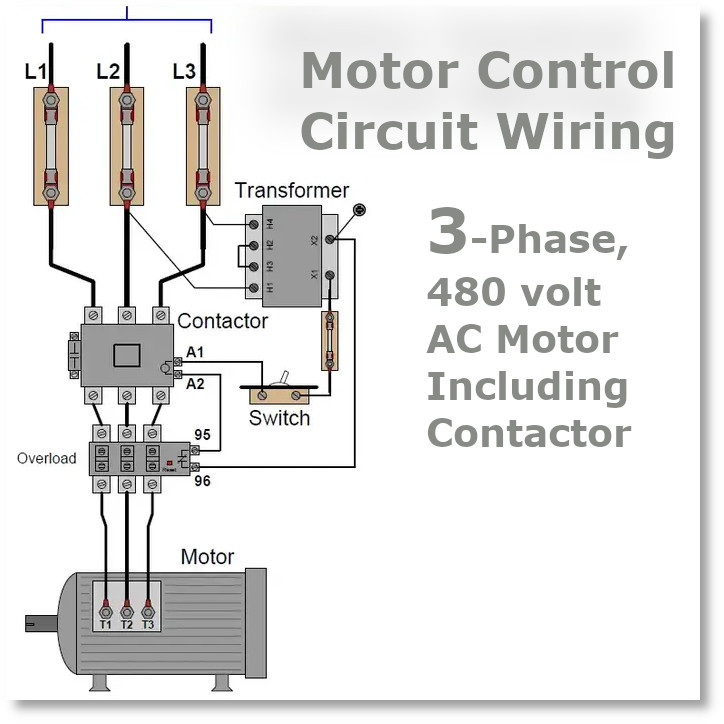
An electrical contactor is the silent powerhouse behind industrial motor control—an electromagnetic switch that acts as a precision on/off toggle for high-current circuits. Unlike basic relays, these workhorses handle up to 200A surges while protecting motors from overloads.
Definition: At its core, a contactor is a magnetically operated switch. Apply voltage to its coil, and it snaps closed; cut power, and it disconnects. This isn’t just switching—it’s controlled power delivery.
Key Components:
- Coil Circuit (A1/A2 Terminals): The brain of the operation. Energize these low-voltage terminals (24V–600V range) to activate the electromagnetic field. Choose the wrong coil voltage, and you’ll fry the control circuit faster than a miswired PLC.
- Power Contacts (L1-L3 & T1-T3): The brawn. These heavy-duty terminals manage the main power flow—L1-L3 connect to your supply lines, while T1-T3 route to the motor. Tighten them to spec (35 lb-ft for 400A lugs), or risk arcing that melts copper.
Analogy: Think of your electrical contactor as the gatekeeper of a 200A highway. Without it, raw power slams into motors unchecked. With it, you get surgical control—starting pumps smoothly or halting conveyor belts mid-cycle. It’s not just a switch; it’s your first line of defense against $18k motor repairs.
6-Step Wiring Process (With Safety First)
1. Power Isolation & Verification
Always start with OSHA-compliant lockout/tagout (LOTO). Verify zero energy using dual-voltage testers—never skip this step. A live circuit here could cost more than downtime.
2. Contactor Selection Guide
Match coil voltage to your control circuit (reverse polarity slashes lifespan by 60%). Choose NEMA for US factories or IEC for global projects—wrong specs risk arc flashes.
3. Control Circuit Wiring
Connect A1 to the control transformer (e.g., 120V) and A2 to the emergency stop. This pair acts as the brain of your electrical contactor, dictating safe startups.
4. Power Terminal Connections
Torque L1-T3 lugs to 35 lb-ft for 400A loads. Test phase rotation with digital sequencers—cross-phasing melts windings in minutes.
5. Overload Relay Integration
Thermal relays (Class 10) trip faster than electronic (Class 20). Undersized relays? Say goodbye to conveyor uptime.
6. Grounding & Initial Testing
Follow NEC 250 for grounding. Suit up in CAT III gear for 480V testing—arc flashes don’t negotiate.
Master these steps, and your electrical contactor becomes a reliability powerhouse—not a liability.
12 Contactor Types Demystified
Not all electrical contactors are created equal. NEMA models (120–600V AC) dominate US factories at 150–150–800, while vacuum contactors (1–15kV) handle mining crushers at 2k–2k–8k. For robotics, solid-state types (12–240V) offer precision control at 300–300–1.2k. Magnetic contactors endure 100k cycles—solid for pumps—but vacuum variants last 500k cycles (ideal for heavy motors) at 10x the cost.
5 Deadly Wiring Errors & Fixes
1. Cross-Phasing
A humming motor that refuses to spin? Cross-phasing is your culprit. Fix it fast with phase sequence correctors—they’ll realign L1-L3 wiring in minutes.
2. Loose Lugs
That 0.1Ω resistance at a terminal lug isn’t trivial—it robs 18% efficiency. Use infrared thermal scans during maintenance to spot heat spikes before they melt insulation.
3. Coil Surge Damage
Voltage spikes above 300% can fry contactor coils overnight. Install snubber circuits (RC networks) across A1/A2 terminals—they absorb surges like a sponge.
4. DIY Grounding Fails
Ungrounded VFDs turn motors into toast. Follow NEC 250: Bond grounding conductors to the contactor’s chassis. No shortcuts—arc flashes don’t warn before striking.
Pro Tip: "These errors cost more than downtime—they risk OSHA fines and fried equipment. Audit your electrical contactor wiring quarterly."
Compliance & Safety: Beyond the Basics
Ignoring electrical contactor safety protocols isn’t just risky—it’s expensive. Under NFPA 70E updates, 480V systems now require 48” arc flash boundaries—that’s four feet of clearance to avoid third-degree burns. For global projects, certifications matter: UL 508 suits North America, while IEC 60947-4-1 dominates European installations. I’ve seen mismatched certifications delay shipments by weeks.
Key Takeaway: "Your contactor’s safety isn’t just about wiring—it’s about aligning with standards that protect both people and profits." Always ground per NEC 250 and suit up in CAT III gear for live testing. Compliance isn’t a checkbox; it’s your shield against six-figure fines.
Conclusion
Your electrical contactor isn’t just a switch—it’s the guardian of motor longevity. Every torque spec, grounded lug, and NFPA-compliant arc flash boundary we’ve covered directly impacts equipment lifespan and operator safety.
Final Takeaway: "Treat contactor wiring like surgery: precise, protocol-driven, and double-checked." A single loose terminal can cascade into $18k repairs, but meticulous adherence to NEC 250 and torque charts prevents disasters.
Call-to-Action: "Print this guide. Laminate the wiring checklist. And never let haste override that coffee-break double-check—your motors (and budget) will thank you."
Master these principles, and your electrical contactor systems become pillars of reliability, not ticking time bombs.
Post time: Apr-21-2025